
A scorecard in sports indicates which team is winning by monitoring an important metric such as number of runs, or baskets or touchdowns. Your business scorecard can provide valuable information on how your organization is doing.
In business, a scorecard is a tool used to measure and track the performance of an organization or specific business unit, department, or individual. It typically includes a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) that you can use to evaluate the success of a particular strategy or initiative.
The scorecard may include both financial and non-financial metrics such as revenue growth, profit margin, customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and productivity. It is used to monitor progress towards specific goals, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to improve overall performance.
Overview: What is a scorecard?
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management tool that is used to measure and track the performance of an organization across four key perspectives: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth. It was developed by Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton in the early 1990s as a response to traditional approaches to measuring business performance that focused solely on financial metrics.
The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard are:
1. Financial perspective
This perspective focuses on the financial performance of the organization, including measures such as revenue growth, profit margin, return on investment, and cash flow.
2. Customer perspective
This perspective focuses on the customer experience and measures such as customer satisfaction, customer retention, and market share.
3. Internal processes perspective
This perspective focuses on the internal processes that are critical to delivering value to customers and measures such as process efficiency, quality, and innovation.
4. Learning and growth perspective
This perspective focuses on the organization’s ability to learn and innovate, and measures such as employee engagement, training and development, and knowledge management.
You may often hear the term dashboard when discussing scorecards. A dashboard and a scorecard are both tools that are used to measure and track business performance, but there are some key differences between the two:
Focus
A scorecard typically focuses on a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) that are used to measure progress towards specific strategic objectives, while a dashboard typically provides a more comprehensive view of business performance across a wider range of metrics.
Presentation
A scorecard typically presents KPIs in a more structured and standardized format, with a clear focus on targets and actual performance data, while a dashboard may present a wider range of metrics in a more visual and customizable format.
Audience
A scorecard is typically used by senior executives and managers to monitor progress towards strategic objectives and make informed decisions, while a dashboard may be used by a wider range of stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, to track performance and make data-driven decisions.
Frequency of updates
A scorecard is typically updated on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, while a dashboard may be updated more frequently, such as daily or weekly, to provide a more real-time view of business performance.
In summary, while both scorecards and dashboards are used to measure and track business performance, scorecards typically provide a more structured and focused view of performance, while dashboards provide a more customizable and comprehensive view of performance across a wider range of metrics.
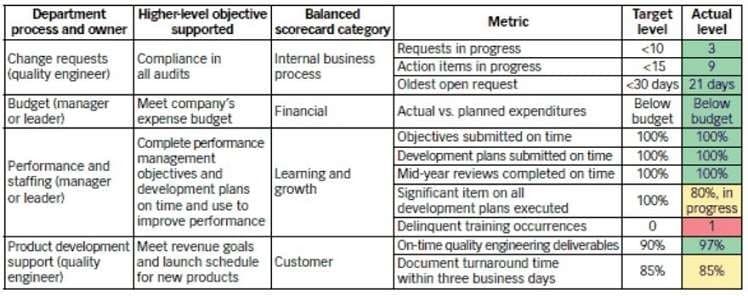
An industry example of a scorecard
The graphic below illustrates how a scorecard might look like. Note the critical information of who owns the metric, the specific category of metric, the actual metric, current metric performance and the targets are all included.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about a dashboard
Here are some frequently asked questions about a scorecard in business:
What is the purpose of a scorecard in business?
A scorecard in business is used to measure and track the performance of an organization or specific business unit, department, or individual. It helps to monitor progress towards specific goals, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to improve overall performance.
What are the key components of a scorecard?
The key components of a scorecard typically include a set of key performance indicators (KPIs), targets, and actual performance data. The KPIs can be financial or non-financial metrics that are used to evaluate the success of a particular strategy or initiative.
What are the benefits of using a scorecard?
Using a scorecard in business has several benefits, including providing a comprehensive view of performance, enabling informed decision-making, identifying areas for improvement, aligning activities with strategic objectives, and improving communication and accountability.
How is a scorecard developed?
To develop a scorecard, businesses need to identify their strategic objectives and the KPIs that are most relevant to measuring progress towards those objectives. They also need to establish targets for each KPI and track actual performance data regularly.
How often should a scorecard be reviewed?
A scorecard should be reviewed regularly, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, to ensure that progress towards strategic objectives is being made and to identify any areas for improvement.