
Quality management is the strategy of continuously improving your organizational processes by setting your goals, identifying deviations from those goals, and then taking appropriate actions to adjust your processes to close the gaps.
Quality management consists of the following four key elements:
Quality Planning – Identifying your quality goals and deciding how to meet them.
- Quality Improvement – Continuously improving all your processes to meet and exceed your customers’ expectations.
- Quality Control and Quality Assurance – According to the American Society of Quality (ASQ), “While Quality Assurance relates to how a process is performed or how a product is made, Quality Control is more the inspection aspect of quality management.”
Overview: What is quality management?
The graphic below illustrates the principles of quality management:
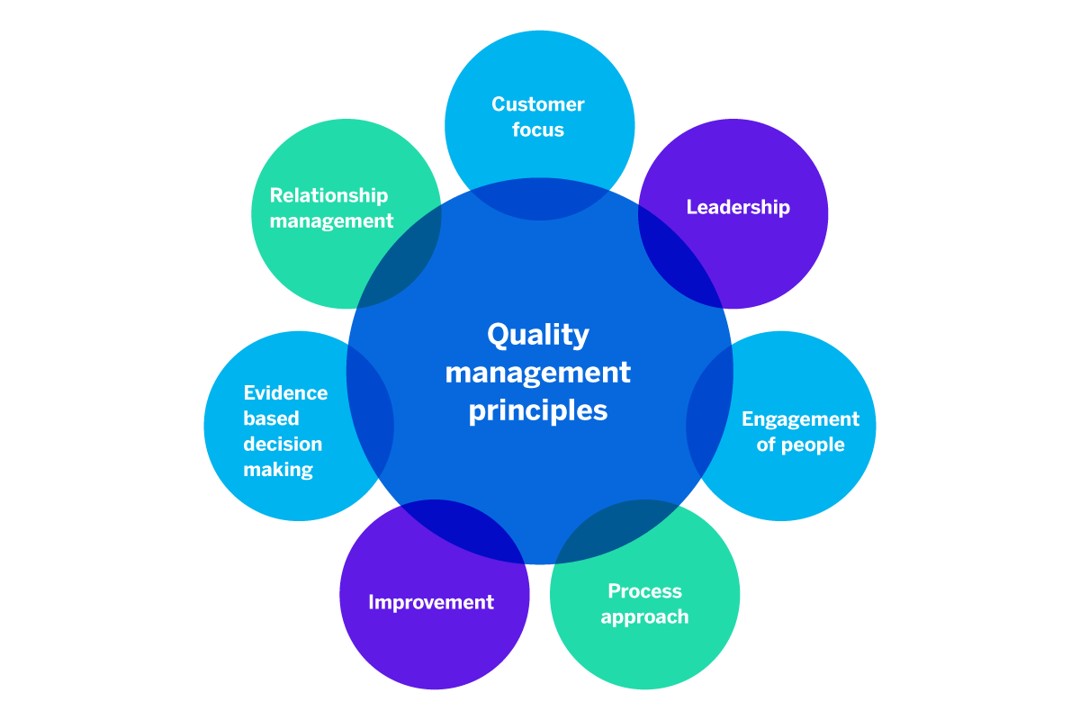
Principles of Quality Management
Here are some further details on each of the principles:
Customer Focus
The primary focus of your organization should be to meet and exceed your customers’ expectations and needs.
Leadership
Strong leadership can establish unity and purpose among your workforce and shareholders thus creating an organizational culture which fosters employee motivation and engagement.
Engagement of People
When employees are wholly engaged, it makes them feel empowered and accountable for their actions.
Process Approach
The approach allows for the understanding that good processes will result in improved consistency, shorter lead times, reduced costs, reduction of waste, and continuous improvement.
Continuous Improvement
Organizations that embed a culture of continuous improvement will see improved performance, organizational flexibility, and an increased ability to take advantage of new opportunities.
Evidence-based Decision Making
Implement data driven decisions throughout your organization.
Relationship Management
Your organization should manage the supply chain process and promote the relationship between your organization and your suppliers to optimize their impact on your organization’s performance.
An industry example of quality management
A large consumer products company decided to implement Lean Six Sigma (LSS) in its largest division. This was done to achieve the benefits of quality management. Below is a graphic of the quality management principles and a discussion of how LSS allowed them to achieve each.
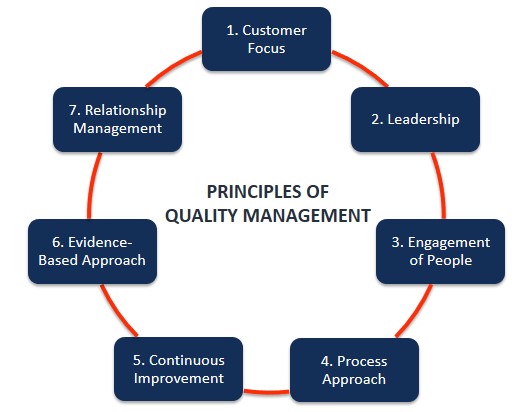
- Customer Focus – Getting Voice of the Customer (VOC) is a critical part of the Six Sigma process.
- Leadership – Six Sigma, if properly implemented, is the responsibility of senior leadership.
- Engagement of People – People from throughout the organization are engaged on the process improvement teams.
- Process Approach – The focus on process is the core of Six Sigma.
- Continuous Improvement – This is the purpose of Six Sigma.
- Evidence Based Approach – Data and statistics are a central part of the DMAIC process.
- Relationship Management – The extended process which includes both suppliers and customers is a vital part of Six Sigma.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about quality management
What are some of the tools that can be used for quality management?
Some tools would include; Kaizen events, Toyota Production System (TPS), Lean Six Sigma, Statistical Process Control, ISO, and Kanban.
What are the four main components of quality management?
The four main components of quality management are: quality planning, quality assurance, quality control and quality improvement.
What are some benefits of quality management?
- It helps an organization achieve greater consistency in their products and services.
- It increases efficiency in processes, reduction in waste, and shorter lead times.
- It helps improve your customers’ satisfaction.
- It creates a culture of continuous improvement of all organizational products, services, processes, and systems.