
DMAIC is an acronym for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control. DMAIC is the process improvement methodology of Six Sigma that’s used for improving existing processes. See DMAIC Methodology.
DMAIC is pronounced: Duh-May-Ick.
What Is DMAIC?
DMAIC refers to a data-driven quality strategy for improving processes, and is an integral part of the company’s Six Sigma Quality Initiative. DMAIC is an acronym for five interconnected phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
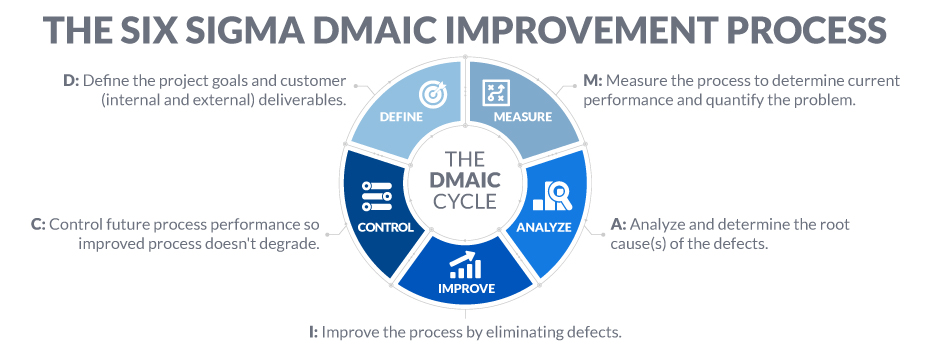
DMAIC Process Steps
Each step in the cyclical DMAIC Process is required to ensure the best possible results. The process steps:
Define the Customer, their Critical to Quality (CTQ) issues, and the Core Business Process involved.
Define who customers are, what their requirements are for products and services, and what their expectations are
Define project boundaries the stop and start of the process
Define the process to be improved by mapping the process flow
Measure the performance of the Core Business Process involved.
Develop a data collection plan for the process
Collect data from many sources to determine types of defects and metrics
Compare to customer survey results to determine shortfall
Analyze the data collected and process map to determine root causes of defects and opportunities for improvement.
Identify gaps between current performance and goal performance
Prioritize opportunities to improve
Identify sources of variation
Improve the target process by designing creative solutions to fix and prevent problems.
Create innovate solutions using technology and discipline
Develop and deploy implementation plan
Control the improvements to keep the process on the new course.
Prevent reverting back to the “old way”
Require the development, documentation and implementation of an ongoing monitoring plan
Institutionalize the improvements through the modification of systems and structures (staffing, training, incentives)
Excerpted From GE’s DMAIC Approach