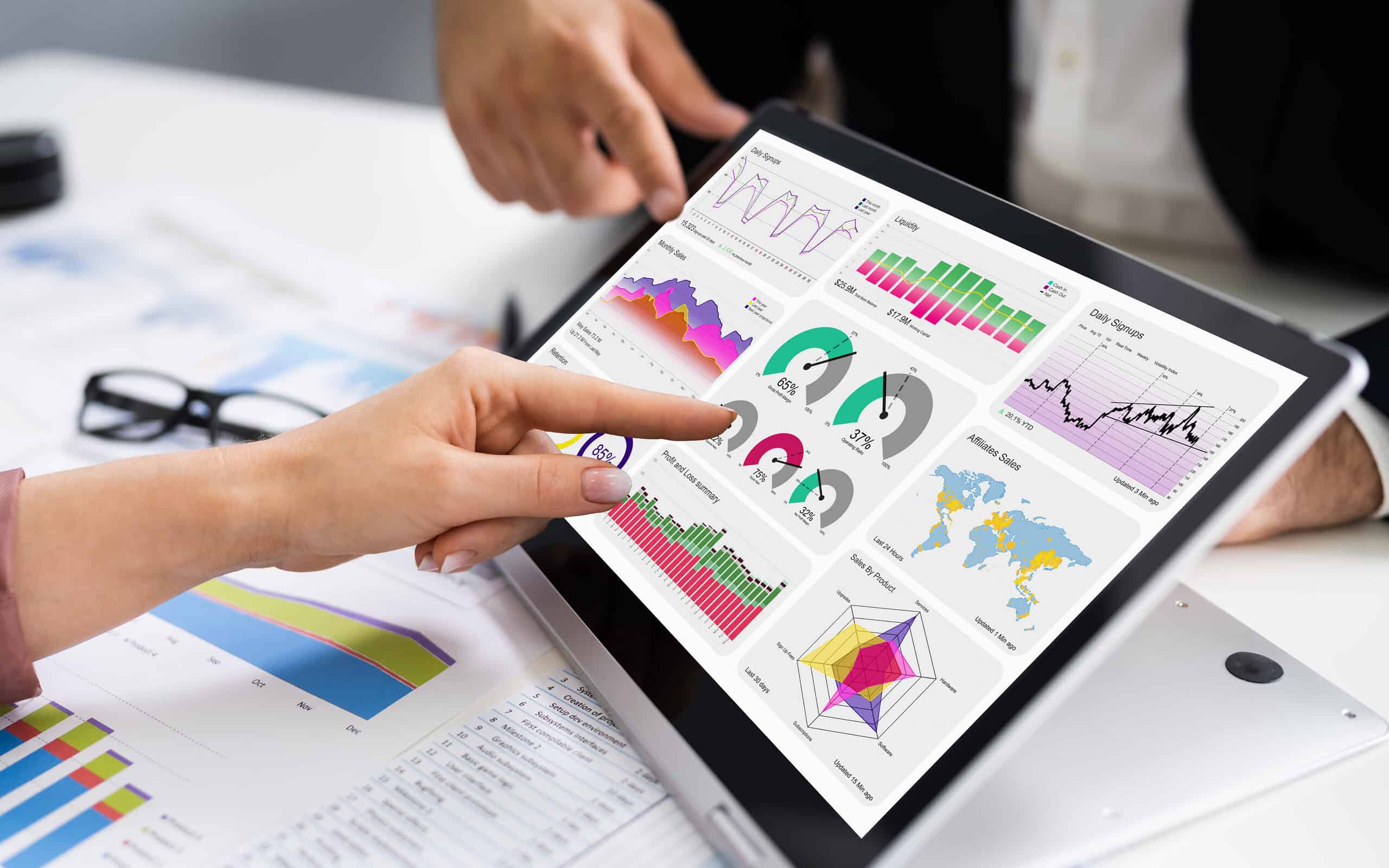
How does your organization track and monitor organizational performance? Do you have key metrics that you frequently look at to make decisions? Using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is a common method for tracking your most important metrics. Let’s see how.
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving its key business objectives. KPIs are used to track performance and progress and can be used to evaluate the success of a particular initiative or project. Examples of common KPIs include revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and employee turnover rate.
Overview: What is a KPI?
KPIs come in many forms and can be used to measure numerous aspects of your organization. Some of the more common ones are:
- Input measures – attributes of resources used in processes that are transformed into process outputs
- Process or activity measures – measure the efficiency, quality, or consistency of processes used to produce an output
- Output measures – measures how much work is done and defines what is being produced or delivered to a customer
- Project measures – informs you about the status of deliverables and milestone progress related to important projects or initiatives
- Strategic measures track progress toward strategic goals, focusing on intended/desired results of the End Outcome or Intermediate Outcome. When using a balanced scorecard, these strategic measures are used to evaluate the organization’s progress in achieving its Strategic Objectives depicted in each of the following four balanced scorecard perspectives:
- Customer/Stakeholder
- Financial
- Internal Processes
- Organizational Capacity
- Operational measures, which are focused on operations and tactics, and designed to inform better decisions around day-to-day product / service delivery or other operational functions
- Risk measures, which are focused on the risk factors that can threaten our success
- Employee measures, which are focused on the human behavior, skills, or performance needed to execute strategy
KPI measures can be either leading or lagging indicators. A lagging KPI measures past achievement, such as annual sales for the previous year. Using lagging indicators to manage your organization is like driving using only the rear-view mirror. A leading indicator is a prediction of what will likely occur in the future. These KPIs are preferred over lagging ones. Your organization might benefit from using a mix of both lagging and leading KPIs.
5 benefits of a KPI
1. Improved decision-making
KPIs provide a clear and measurable way to track the performance of a business, which can help managers and leaders make more informed decisions.
2. Increased accountability
By setting clear and measurable goals, and tracking progress towards those goals, KPIs can increase accountability among employees and teams.
3. Increased focus
By identifying and tracking the most important aspects of a business, KPIs can help to focus the efforts of employees and teams on the areas that will have the greatest impact on overall performance.
4. Identifying improvement areas
KPIs can help identify areas that need improvement, providing insights and direction for business improvement initiatives.
5. Benchmarking progress
KPIs allow for comparison of current performance to past performance, industry standards, and/or competitors, helping to identify areas of progress and areas of weakness.
Why is a KPI important to understand?
Here are a few thoughts regarding the importance of understanding how to use your KPIs.
It is for tracking performance, not punishing people
Tracking your KPIs will allow you to understand how your organization is performing, so you can make proper decisions. If you use your KPIs to punish people when the numbers aren’t what you expected, you may no longer be able to trust your numbers because people may start reporting them incorrectly to protect themselves.
Don’t measure everything that moves
The K in KPI refers to Key. Select the key metrics you wish to monitor and track those.
KPI tracking should be linked to the appropriate levels of the organizations
A CEO should not be looking at daily KPIs. Your organization will have strategic, tactical, and operational metrics. Who looks at them and at what frequency should be appropriate to prevent overmanaging and overreacting to changes in the KPIs.
An industry example of a KPI
One industry example of using a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is in retail. One common KPI used in the retail industry is same-store sales growth which compares sales from a specific store or group of stores over a certain period of time (often year over year). This KPI provides a clear and measurable way for retailers to track the performance of their stores and can help managers and leaders make more informed decisions about things like inventory management, staffing levels, and marketing strategies. It also can be used as a benchmark to compare performance with competitors.
Another example is customer satisfaction and customer retention, which measure how well a store is meeting the needs of its customers. Retailers may survey customers to gather data on factors like product selection, store layout, and customer service. This KPI is important because it can indicate if customers are likely to return to the store or recommend it to others.
8 Best practices when thinking about a KPI
Here are several tips for effectively utilizing KPIs in your organization:
1. Align KPIs with business objectives
Make sure that the KPIs you choose align with your overall business objectives and support your overall strategy.
2. Keep them simple
Avoid using too many KPIs, instead focus on a few key metrics that are most important to your business.
3. Make them measurable
Choose KPIs that are quantifiable and can be tracked over time.
4. Communicate them effectively
Ensure that everyone in the organization understands the KPIs and how they will be used.
5. Monitor and review regularly
Regularly track and review the performance of your KPIs, and adjust them as necessary.
6. Involve employees
Involve employees in the process of setting and tracking KPIs, this will increase their engagement and accountability.
7. Use them as a guide not a rule
KPIs should be used as a guide to help you understand the performance of your business, not as a rule to be followed blindly.
8. Keep them in context
Remember to put the KPI in context. They should be seen in relation to other factors that could influence their results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about a KPI
What is a KPI?
A KPI is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an organization is achieving its key business objectives.
How do I choose the right KPIs for my business?
The right KPIs for your business will depend on your specific goals and objectives. It’s important to choose KPIs that align with your overall strategy and that are relevant to your industry.
How often should I review my KPIs?
The frequency of reviewing KPIs will depend on the nature of your business and the specific KPIs you are tracking. Some KPIs may need to be reviewed on a daily or weekly basis, while others may only need to be reviewed monthly or quarterly.
Let’s wrap this up
The acronym, KPI, stands for Key Performance Indicator. It’s a measure of how projects, individuals, departments, or businesses perform in terms of strategic, tactical, and operational goals and objectives.
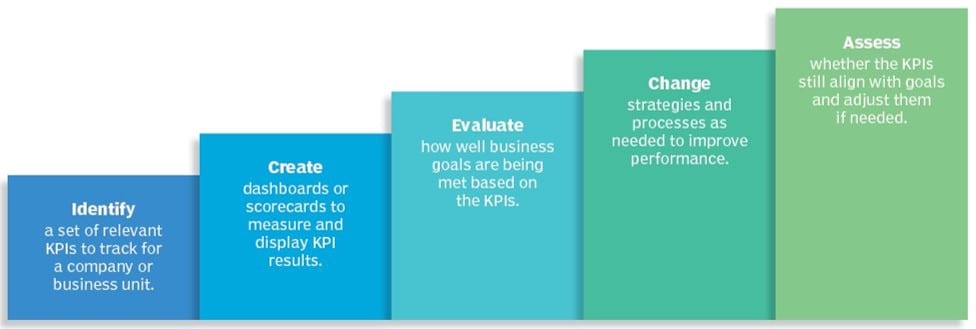
Below are the steps your organization can use to develop your own organizational KPIs: