A company with a Six Sigma deployment identifies a process improvement area within the business. It is easy to figure out what comes next – just define the problem, set the goal, select the project team, pick the team leader and get out of the way. Right? Well, sort of…but before deployment leaders get the project rolling, they must first make sure they have chosen the right project – one which is in line with business priorities.
If a wrong project is selected, it may not have the full business buy-in, project bottlenecks may not be removed due to other business priorities, the project team may be frustrated and the end result may be that the project has to be scrapped, or, if the project is completed, the business may not feel a positive impact. It is a lose-lose situation for all involved in the process improvement effort, especially for the Six Sigma sponsor or Champion who can lose credibility with team members and company leaders alike. So how can one make sure projects selected are in line with business priorities?
Project selection is one of the most critical and challenging activities faced by Six Sigma companies. In most companies, difficulty arises in sizing and packaging opportunities to create meaningful projects. To be successful, the project selection process must be well defined and disciplined. A three-step approach can assure a successful project selection process. The steps are:
Step 1: Identify the relative importance of strategic business objectives
Step 2: Identify the relative importance of specific key business processes
Step 3: Calculate the relative importance of key metrics of key processes
Step 1
The purpose of Step 1 (Table 1) is to understand business in depth and to focus on business priorities. The process is:
a. Compile the company’s list of strategic business objectives (SBO).
b. Weight the impact of each SBO on gross profits on a 1-to-5 scale (1 = low impact, 5 = high impact).
c. Assess the current status and entitlement of each SBO on a 1-3-9 scale (1 = not in control, 3 = partially controlled, 9 = in control).
d. Calculate the gap between the current status and entitlement for each SBO.
e. Assess the feasibility of significant improvement using 1-3-9 scale (1 = difficult to improve, 3 = moderate effort to improve, 9 = easily improved).
f. Assess the impact of SBO on gross profits on 1-3-9 scale (1 = low impact, 3 = moderate impact, 9 = high impact).
g. Calculate the absolute rating by multiplying gap and feasibility and weighted impact on gross profits.
h. Add all the absolute ratings to get a grand total of absolute ratings.
i. Calculate the relative importance of each strategic business objective by dividing its individual absolute rating by the grand total absolute rating.
The outcome of Step 1 is that from its list of strategic business objectives, the company can identify the key strategic business objectives that can be considered for Six Sigma project selection.
| Table 1: Relative Importance of Strategic Business Objectives | |||||||
|
Strategic |
Impact |
Current |
Entitlement | Gap |
Feasibility |
Absolute |
SBO |
|
New Product Development Effectiveness |
5 |
1 |
9 |
8 |
1 |
40 |
0.14 |
| Presales Customer Education |
4 |
1 |
9 |
8 |
1 |
32 |
0.11 |
| Customer Communication |
3 |
3 |
9 |
6 |
1 |
18 |
0.06 |
| Attrition of Business Partner |
2 |
3 |
9 |
6 |
3 |
36 |
0.13 |
| Customer Service Level Inconsistency |
5 |
1 |
9 |
8 |
3 |
120 |
0.42 |
| Custmer Churn |
5 |
1 |
9 |
8 |
1 |
40 |
0.14 |
| X | |||||||
| Y | |||||||
| Z | |||||||
|
Grand Total |
286 |
||||||
Step 2
Step 2 (Table 2) shifts the focus from strategic business objectives to processes that impact the key business objectives. The process for Step 2 is:
a. Compile list of business processes existing within the business.
b. Link each process with each SBO on 1-3-9 scale (1 = no relationship, 3 = some relationship, 9 = high relationship).
c. Calculate each process’s importance rating – the product of SBO relative importance and each process relationship with SBO.
d. Calculate the absolute importance rating for each process by adding all the individual importance ratings for that process.
e. Calculate the grand total absolute process importance rating by adding the absolute ratings for all processes.
f. Figure relative process importance rating by dividing individual absolute importance ratings for each process by the grand total absolute process importance rating.
| Table 2: Relative Importance of Specific Key Business Processes | |||||||||
|
Strategic |
SBO |
Pre- |
Pre- |
Billing & |
Billing & |
Retention |
Retention |
Call |
Call |
|
New Product Development Effectiveness |
0.14 |
3 |
0.42 |
1 |
0.14 |
3 |
0.42 |
1 |
0.14 |
|
Presales Customer Education |
0.11 |
9 |
1.01 |
1 |
0.11 |
1 |
0.11 |
3 |
0.34 |
|
Customer Communication |
0.06 |
3 |
0.19 |
3 |
0.19 |
3 |
0.19 |
9 |
0.57 |
|
Attrition of Business Partner |
0.13 |
1 |
0.13 |
1 |
0.13 |
1 |
0.13 |
1 |
0.13 |
| Customer Service Level Inconsistency |
0.42 |
3 |
1.26 |
9 |
3.78 |
1 |
0.42 |
9 |
3.78 |
| Custmer Churn |
0.14 |
3 |
0.42 |
9 |
1.26 |
9 |
1.26 |
9 |
1.26 |
| X | |||||||||
| Y | |||||||||
| Z | |||||||||
| Absolute Process Importance (Grand Total = 17.74) |
3.42 |
5.60 |
2.52 |
6.20 |
|||||
| Relative Process Importance |
0.19 |
0.32 |
0.14 |
0.35 |
|||||
Step 3
The purpose of Step 3 (Table 3) is to further drill down from processes to key metrics that add value to the business. After identification of metric by using this approach, one can get business insights that help when it comes time to select projects for improving business processes. The process for Step 3 is:
a. Compile the list of key metrics for each process.
b. Assess the current baseline and entitlement for all metrics on 1-3-9 scale (1 = not in control, 3 = partially controlled, 9 = in control).
c. Calculate the gap between the current status and entitlement for each metric.
d. Calculate relative metric importance by multiplying gap and relative process importance rating.
| Table 3: Relative Importance of Key Metrics of Key Processes | ||||||
|
Process |
Relative |
Metric |
Current |
Entitlement | Gap |
Relative |
|
Presales |
0.19 |
Sales Rep’s Score on New Product |
1 |
9 |
8 |
1.52 |
|
Billing & Dispatch |
0.32 |
Percent Billing Complaints |
9 |
9 |
0 |
0.00 |
|
Retention |
0.14 |
Percent Conversion – Proactive Retention |
1 |
9 |
8 |
1.12 |
|
Call Center |
0.35 |
Call Per Sub |
3 |
9 |
6 |
2.10 |
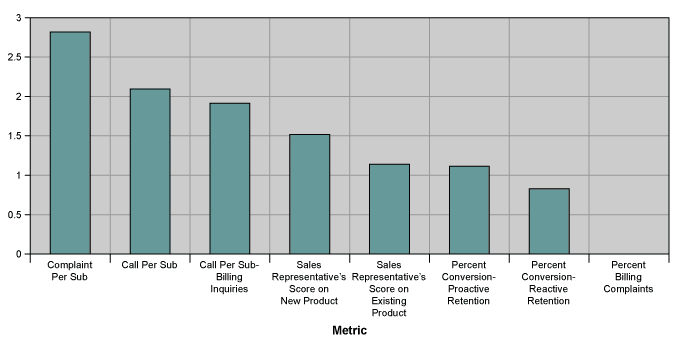
Based on the relative metric importance, a chart (like the one below) can show which metrics are important to be considered for Six Sigma projects that can help the company meet its strategic business objectives.