IDOV is one of the methodologies associated with Design for Six Sigma (DFSS). We will discuss the IDOV methodology, how it contrasts with other DFSS approaches, its benefits, and some tips on how to best use the tool.
Overview: What is IDOV?
Six Sigma is an improvement philosophy and methodology for improving all the processes in your organization. The two major approaches and methodologies are DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) and DFSS.
DMAIC is designed to improve processes in a continuous and incremental manner. DFSS focuses on significant redesign of a product or process as well as the design of a new product or process with the intent of achieving a defect-free or Six Sigma level of quality.
There are a number of different methodologies under the DFSS umbrella. Here is a list of common acronyms and their definitions.
- DMADV: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify
- IDDOV: Identify, Define, Develop, Optimize, And Verify.
- DCOV: Define, Characterize, Optimize, Verify
- IDOV: Identify, Design, Optimize, Validate
- DCCDI: Define, Customer, Concept, Design, Implementation
- DMEDI: Define, Measure, Explore, Develop, Implement
- DMADOV: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Optimize, Verify
- ICOV: Identify Requirement, Characterize, Optimize, Verify
- CDOV: Concept Development, Design Development, Optimization, Verify Certification
- IIDOV: Invent, Innovate, Develop, Optimize, Verify
- IDEAS: Identity, Design, Evaluate, Assure, Scale-Up
While they all have a slightly different definition, they essentially follow the same core process. Below is a chart showing the four most widely used approaches and a comparison with DMAIC.
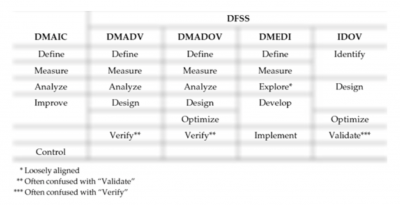
Comparison of DMAIC and four common DFSS methods
Now that you have context and background on DFSS, let’s explore IDOV in more detail.
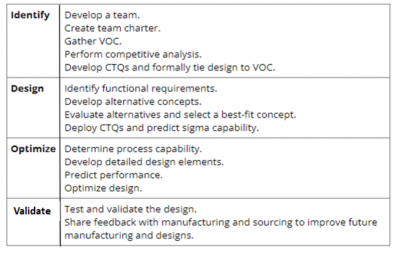
Identify phase
The Identify phase starts off by linking the proposed design need to the voice of the customer (VOC). During this phase, you will form a team, develop the project charter, gather VOC, do competitor benchmarking, and develop your critical to quality characteristics CTQs.
Deliverables:
- Identify your specific customer and process/product requirements
- Write your business case
- Identify technical requirements by developing specifications for your CTQs
- Establish roles and responsibilities, and develop a RACI (responsibility, accountability, consult, inform) diagram
- Develop timelines and milestones
Tools:
- QFD (Quality Function Deployment)
- FMEA (Failure Means and Effects Analysis)
- SIPOC (supplier, input, product, output, customer) map
- Target costing for new product design
- Competitor Benchmarking
Design phase
Based on the CTQs, the design phase seeks to identify product functional requirements, alternative concepts, and the selection of a best-fit concept. The sigma level will be predicted to be sure you are reaching your Six Sigma, or defect-free, quality level.
Deliverables:
- Lock down the final concept design
- Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies using FMEA
- For each technical requirement, identify specific design parameters
- Develop a plan for any needed raw material or component acquisition
- Manufacturing plan
- Use statistical tools such as DOE (design of experiments) to determine the relationship between CTQs and your technical requirements
Tools:
- Risk assessment
- FMEA
- Engineering analysis
- Material vendor analysis
- Simulation
- DOE (design of experiments)
- Systems engineering
- Analysis tools
Optimize phase
The optimize phase requires use of process capability information and a statistical approach to tolerancing. In this phase, you will develop detailed product design elements, predict performance, and optimize the final design. Using process capability analysis, you will establish appropriate design tolerances.
Deliverables:
- Assess process capabilities to meet critical design parameters and CTQs
- Design for robust performance and reliability under a variety of different conditions
- Poka Yoke or error-proofing
- Compute tolerance limits
- Optimize your sigma level and development cost
Tools:
- Design for manufacturing (DFM)
- Process capability (Cpk, Ppk, Cp, Pp)
- Robust design
- Monte Carlo simulations (Crystal Ball)
- Tolerancing
- Six Sigma tools
Validate phase
The validate phase activities consist of testing, piloting, and validating the design.
Deliverables:
- Prototype test, pilot, and validation of whether design requirements can be met
- Assess performance, failure modes, reliability, and risks
- Design and redesign revisions as needed
- Final project review, sign-off, and a control plan
Tools:
- Accelerated testing
- Reliability engineering
- FMEA
- Control plan
3 benefits of IDOV
As a structured and formal process for design, IDOV has a number of benefits. Here are a few.
1. Captures the voice of the customer and critical to quality elements
IDOV starts with the needs of the customer and designs the process or product to meet those needs. DMAIC starts with the existing process and seeks to incrementally improve it. That is why IDOV is a better approach for developing something new.
2. Design for process capability
Starting with the desired quality level in mind, IDOV then allows you to design the product or process to achieve that level.
3. Risk assessment
Risk assessment and mitigation are an integral part of IDOV, allowing the final outcomes to be as successful as reasonably possible.
Why is IDOV important to understand?
This process requires discipline and structure, so it is important to understand the deliverables and tools needed to properly manage an IDOV project.
Best used for new design, not redesign
There are Six Sigma methods for incrementally improving or redesigning an existing product or process. IDOV is best suited for starting from scratch rather than for an incremental change.
Driven by specific customer requirements
The first two steps of IDOV, identify and design, are driven by the VOC’s specific requirements. The other two steps, optimize and validate, focus on how to develop and produce the product to meet those specific requirements at a defect free level of quality.
Once the product is designed, you need to be able to profitably produce it
Designing the perfect product to meet your customer’s requirements and be defect-free is one challenge. Being able to produce it in an efficient and cost-effective way is also a big challenge. There must be balance.
An industry example of IDOV
After multiple incremental redesigns of its bottle, a beverage company decided to use IDOV to create a revolutionary and first-of-its-kind bottle.
In the identify phase, the company organized a cross-functional team representing the functions of marketing, manufacturing, sales, quality, R&D, and Lean Six Sigma. Their initial tasks were to gather VOC and CTQs directly from the customer and to benchmark any competitors who might have a similar design. They hired a survey firm to team with their people.
The team used the information gathered in the design phase, along with VOC, CTQs, and benchmark data, to develop detailed product requirements and technical considerations. A set of initial product design drawings were made. The design alternatives were then evaluated and compared against each other on the basis of cost, achievable quality, manufacturability, efficiency, schedules, milestones, and available resources. With this information, the team selected the best product design drawing that met both the customer’s requirements as well as internal requirements.
In the optimize phase, the team took the chosen product design and finalized the product specifications. The specifications and product design drawings were given to manufacturing, who was responsible for acquiring any special equipment and raw material vendors. Quality was tasked with implementing an error-proofing process necessary to assure a defect-free product.
Once the production system was set up by manufacturing, the team conducted a series of tests using prototypes as part of the validate phase. They also did some test marketing of the new design. If there were any defects in the manufacturing process, they were identified and corrected.
Senior leadership made the decision to release the new bottle, and the design along with the new liquid beverage was a major commercial success.
3 best practices when thinking about IDOV
Executing an IDOV project is a bit different than the traditional DMAIC project. Keep these tips in mind when deciding to use the IDOV methodology.
1. Get the right people on the team
IDOV requires creativity and technical expertise to come up with a creative design meeting all customer product design requirements at a defect-free level of quality. Select a team of highly skilled people. Since the intent is to create and produce something new, the in-depth process knowledge required for a DMAIC project is not as critical to the success of the IDOV project.
2. Spend adequate time on gathering the VOC and CTQs
Your new design will be a reflection of the VOC and CTQs of your customer. Do not shortcut this critical step.
3. Engage manufacturing and quality functions early in the design
There are three critical components of IDOV. First is the design. Second is the manufacturability of the design. Finally, there is the quality of the final product. Get the manufacturing and quality functions involved early in your design phase to prevent rework and redesign later on.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about IDOV
What does IDOV stand for?
It is one of the DFSS methods and stands for identify, design, optimize, and validate.
What is the difference between DMADV and IDOV?
There is no real difference between the two. Both have the goal of developing defect-free quality products and processes designed to meet specific design requirements driven by the voice of the customer and their critical-to-quality attributes.
What is the difference between DMAIC and IDOV?
Improvements can be of two types: incremental and continuous improvement of an existing process or product or designing a new process or product. You will use DMAIC when you want to improve an existing process or product. If you are designing a new process or product, you can use IDOV or one of the other similar DFSS methodologies..
IDOV summary
IDOV is one of the DFSS methods used for achieving breakthrough improvement by designing new processes and products to meet specific customer design requirements at a defect-free level of quality. Below is a summary of the deliverables from each of the four phases of IDOV.