
The Define Phase
The senior leadership of the IT services company completed the important pre-project work and found an area of the business worthy of attention by a DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) project team. The team then began work on understanding and articulating the project goals, scope and business case.
The DMAIC roadmap called for work in these areas during the Define phase:
D1. Project Charter: Spelling out the project’s goal statement.
D2. Customer Requirements: Identifying all the internal and external customers who depend on the outputs of the process under study, the deliverables and measures connected with those outputs, and the process steps, process inputs and (as appropriate) the suppliers of those inputs.
D3. High Level Process Map: Showing the flow of information, materials and resources, from key process inputs, through process steps and decision points, to create the process outputs. The map describes the flow of what happens within the scope of the target process and it defines the boundaries of that scope.
D1. Project Charter
Here are some of the key elements of the project charter.
Problem Statement: “Competitors are growing their levels of satisfaction with support customers, and they are growing their businesses while reducing support costs per call. Our support costs per call have been level or rising over the past 18 months, and our customer satisfaction ratings are at or below average. Unless we stop – or better, reverse this trend – we are likely to see compounded business erosion over the next 18 months.”
Business Case: “Increasing our new business growth from 1 percent to 4 percent (or better) would increase our gross revenues by about $3 million. If we can do this without increasing our support costs per call, we should be able to realize a net gain of at least $2 million.”
Goal Statement: “Increase the call center’s industry-measured customer satisfaction rating from its current level (90th percentile = 75 percent) to the target level (90th percentile = 85 percent) by end of the fourth quarter without increasing support costs.”
The project team also developed its initial set of milestones, tasks, responsibilities, schedule and communication plan. After reviewing the charter with their Champion, team members began work on the next step – customer requirements.
D2. Customer Requirements
For many processes there are one or more customers who are obvious – the people who pay for products or services or those who visibly depend on the company, like employees. Often, though, there are internal and external customers and dependencies that are not so obvious. A SIPOC table (suppliers, inputs, process, outputs and customers) develops a detailed view of all the important customers, their requirements, and the related process step and supplier dependencies.
SIPOC Table:The team developed a SIPOC table to help identify and report what it learned about key customers and their requirements. While processes flow in the SIPOC direction, the thought process used to build the table often begins with the customer, suggesting display in the COPIS (customer, output, process, inputs and suppliers) direction as shown in Figure 1.
Voice-of-Customer (VOC) Interviews: The SIPOC table highlighted some areas where more information about the process – as understood by customers and call center staff – would be helpful. Representative samples of the company’s customers were involved in group interviews. The following are excerpts from individual customer responses and are representative of the data gathered. The answers are to the question: “What influences your level of satisfaction with our services?”
Group 1
A1. “Well, first and foremost I want the correct answer to my questions or issues. It makes me nuts when I’m told something that turns out later to be wrong or only part of the story.”
A2. “I really like it when the person who answers the phone has a good attitude. Sometimes you can just tell they wish you’d just go away and stop bothering them with stupid questions.”
A3. “Well I can sure tell you what I don’t like. That voice response thing where they ask you to make 46 choices (and none match what you want) is a real pain – ends up taking a lot of my time and then they seem to ignore it all anyway and ask the same questions again. What’s the point? Sometimes I wonder if they ever asked a real customer to test these things before they put them in.”
A4. “I’m happy when my call gets answered quickly and the person I talk to knows their stuff and gives me an answer on the first call. When I have to wait for a call back and talk to someone else, repeating some of the same stuff – that’s a real drag!”
A5. “I like it when the person on the phone can actually make a decision without putting me on hold while they get an ok from a supervisor. Seems like they spend 10 minutes to make a $5 decision. That just doesn’t make sense to me. Seems like some control freak is running the show.”
A6. “Follow-through is what really matters to me. I don’t necessarily expect you’ll always be able to resolve my issue immediately, but I do expect you’ll call me back in a reasonable amount of time.”
A7. “My hot button is getting someone who has enough patience to really solve my problem. Some of this stuff seems pretty technical to me, and I don’t always know even the right question to ask. I like it when the person on the phone cares enough to get to the real solution, even when I can’t explain exactly what I need.”
A8. “I don’t want to be transferred around. Last time I called I got transferred four times and ended up with the same person I started with. I’m too busy to put up with that!”
Group 2
A1. “Our big concern is speed. Our customers demand answers from us, and we in turn rely on you for some of that. That means you have to be adequately staffed to meet call volume.”
A2. “What we most need from you is people who can answer complicated questions accurately and quickly – not just the easy stuff, we can do that ourselves.”
A3. “We need you to have immediate access to up-to-date information about all of our accounts and transactions with all of your branches and locations. It creates huge problems for us when your records aren’t accurate and timely. We can’t sit on hold for 10 minutes.”
A4. “I call 3 to 4 times a week, and the thing I find most frustrating is the lack of consistency. Sometimes my call gets answered in 2 minutes, which I can live with, and sometimes it’s 10, which I can’t. I also notice that there’s a lot of variation in how long it takes to get answers to very similar issues. I call your competition all the time also, and they’re a lot more consistent.”
Summarizing Customer Requirements: The team began to summarize what it was learning about what’s important to customers – in the form of requirement statements and measures.
| >Requirements | > Measures |
| > Quickly connect with a helpful person | > Wait time |
| > Get the information I need | > Transfers, service time |
| > Apply the information, with help if needed | > Customer satisfaction, support cost |
| > Understand how to avoid problems recurring | > Days to close |
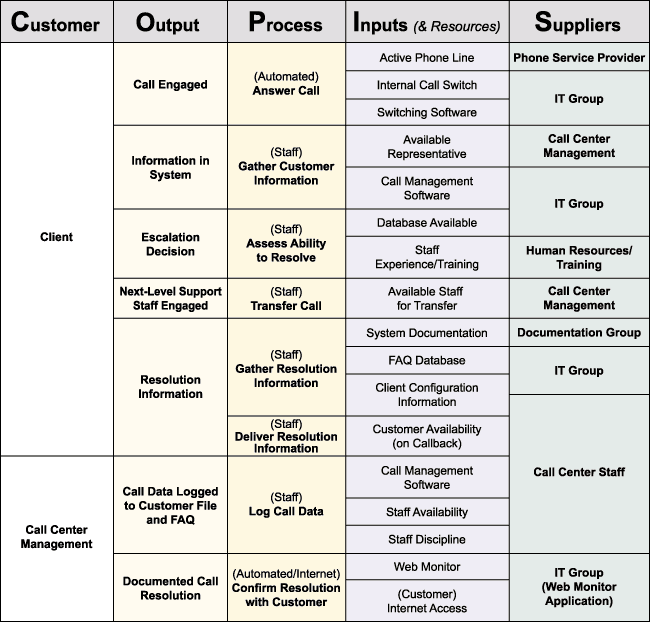
D3. High Level Process Map
The team mapped the process by which an initiating event (an issue encountered by a customer) moves into and through the resolution process (Figure 2).

The process map will be helpful during the Measure phase, as the project team considers how and where to gather data that will shed light on the root cause of the issues most pertinent to the project’s goals.
Part 3 is about the Measure phase of the project.