
Process management, sometimes referred to as Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to ensure that your organization’s business processes are aligned in an efficient and effective manner, and aligned with your organization’s strategic goals.
Some of the benefits to having a process management system in place are:
- Flexibility – Business environments are not stagnant. They are constantly changing and your organization needs to be flexible to adapt to these changes.
- Efficiency – Efficient processes will optimize the use of your resources.
- Visibility – Your employees will have better visibility of how your organization functions and how everything is linked.
- Increase revenue and profits – Process management may result in cost savings and increased revenue, resulting in stronger business performance.
- Employee engagement – Involving your employees in the development and execution of process management may result in increased employee engagement and involvement.
- Culture of continuous improvement – Embedding an effective process management approach and using such methods as DMAIC may help instill a culture of continuous improvement in your organization.
Overview: What is process management?
The steps of implementing a process management system are:
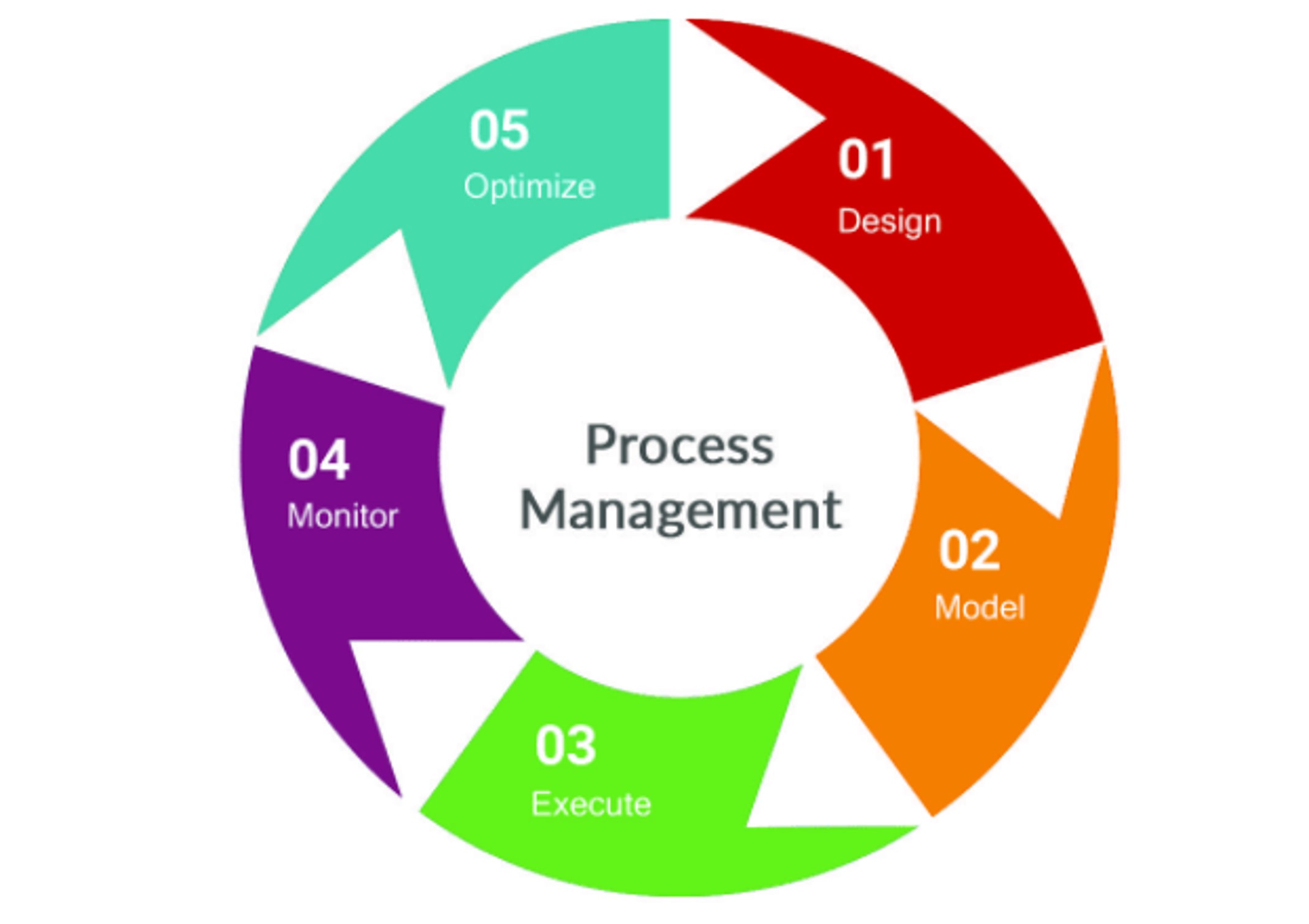
Analyzing
Collecting data on key performance indicators (KPI) indicates which processes are the least efficient. You can use qualitative and quantitative data to reach your conclusions. You may also do customer value-added analysis to measure each process’s contribution to the business.
Designing/Modeling
During this step, you can process map your current state processes using such tools as SIPOC, Swimlane Maps, Top-down maps and Value Stream Maps (VSM).
Implementing
It’s now time to implement and execute any changes and improvements to your processes.
Monitoring
Gather information about whether the improved processes are effective and whether the expected improvements had the desired impact on reaching your business goals.
Optimizing
At this stage, you’ll continually refine the process based on information gathered in the monitoring stage and as the business changes over time. If needed, you may need to design a new process by using such tools as DMEDI or DMADV.
An industry example of process management
Here are some examples where process management can be used:
- Onboarding New Employees
- Managing Logistics
- Loan Processing
- Compliance Management
- Customer Service
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about process management
Is process management and project management the same?
No. Here is a table contrasting process and project management:

What is the purpose of process management?
Process Management is a structured approach that provides tools and resources for analyzing, defining, optimizing, monitoring, and controlling business processes. It helps align your processes with your organization’s strategies and objectives.
What are the stages of process management?
They are analyzing, designing/modeling, implementing, monitoring, and optimizing.