
Lean Six Sigma (LSS) is usually not taught until college, but middle and high school students can learn and apply these techniques to solve problems and make significant improvements. This two-part article will look at one school taking the lead and certifying younger students as White Belts. Part 1 focused on an overview of the program. Part 2 reviews the eight projects that the students completed.
The LSS projects of the students* in Cary, North Carolina, ranged from cooking, to party planning, to marketing, to tourism and more; they were a mix of actual and hypothetical projects. The project teams shared a common set of tools for all of the projects – process maps, histograms, Pareto charts, standard work and scatter plots.
Project 1: Improve Apple AirPod Sales (Hypothetical)
Problem statement: In the United States, customers are not buying Apple AirPods for multiple reasons including sound quality, lack of color options and the concern that the earbuds will fall out.
Goal statement: To raise Apple AirPod sales by applying DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control).
Solutions:
- Use less expensive plastic to make the outer shell. By saving money on the outer shell, Apple can spend that money to upgrade the sound quality. This will draw in the customers who said that the sound quality wasn’t good.
- Make the plastic shell different colors for the people who wanted variation in the look of the pods. This is an easy implementation based on the money saved on the type of plastic being used.
- Add hooks for the AirPods, so the buds sit tighter in people’s ear, making them less likely to fall out.
Results: This would lower the price from $159 to a range of $140 to $155, resulting in a 20 percent increase in sales.
Project 2: How to Successfully Host Your Next Birthday Party (Real)
Problem statement: Birthday parties in 2017 were a failure because 75 percent of the kids left within 60 minutes of the start.
Goal statement: For 2018 birthday parties, kids should stay for at least 120 minutes.
Solution: Birthday party hosts offered more game choices, offered a better music selection, more air conditioning and generated more involvement with hands-on activities.
Results: The number of kids leaving parties early decreased from 75 percent of attendees to 25 percent of attendees.
Project 3: Cake It Up (Real)
Problem statement: Baking a cake takes too long at an average of 172 minutes, and the average taste score of cakes is only 3 out of 10 (22 people surveyed).
Goal statement: Bake a cake that takes less than 120 minutes and achieve a taste score of 7 out of 10.
Solution: Conducted three trials. The recipe was standardized and the instructions were carefully followed while baking.
Results: The baking was reduced from 172 minutes to 105 minutes. The new and improved recipe increased the average taste score from a 3 to an 8.
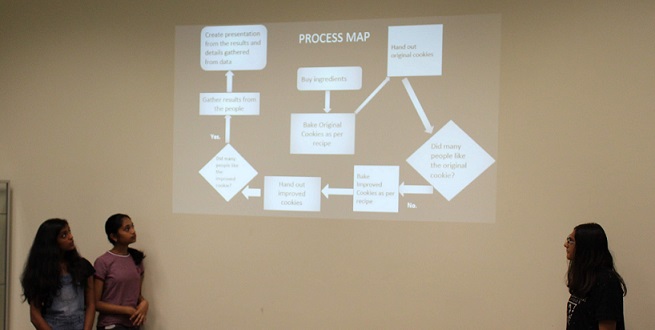
Project 4: Improve Taste of Classic Chocolate Chip Cookie (Real)
Problem statement: The baking of the original recipe resulted in a dry and brittle cookie. In addition, the making of the cookies took a long time – approximately 45 minutes.
Goal statement: At least 80 percent (12 of 15) people who taste the two different recipes will prefer the improved (moister) cookie over the original in taste. The preparation time will be reduced to 30 minutes.
Solution: Use the original recipe with the following adjustments: leave out salt, use salted butter and make cookies smaller than directed (the smaller the cookies, the less time it takes to bake). Bake them in the oven for 5 minutes, rather than 8-10 minutes, for a less crunchy and crumbly cookie.
Results: The total time needed to bake the cookies went from 45 minutes to 28 minutes. Thirteen out of 15 people preferred the cookies made with the improved recipe, exceeding the goal of 80 percent.
Project 5: Dunkin’ Donuts Location (Hypothetical)
Problem statement: In which town should Dunkin’ Donuts open a new store – Cary or Morrisville, North Carolina? The store will need to produce a profit in 18 months as well as satisfy customers and thrive amid its competition.
Goal statement: Find the best town to open a Dunkin’ Donuts franchise. Make $50,000 in profit within 18 months, while satisfying customers through excellent service and products.
Solution: Used criteria such as population, minimal competition, total cost of ownership, average spend per customer and product mix to derive estimated revenue and profits for each potential location.
Results: Cary would generate revenue of $1.3 million and a profit of $320K. Morrisville would generate revenue of $970K and a profit of $28K. Therefore, Dunkin’ Donuts should open a new store in Cary.
Project 6: Attract Tourism to World’s Least Visited Country (Hypothetical)
Problem statement: Nauru (an island in Micronesia) is the world’s least visited country. It has 11,000 residents with only 200 tourists per year. Nauru’s neighbor, the Solomon Islands, get 20,000 visitors a year. What went wrong with Nauru?
Goal statement: Increase the number of tourists visiting Nauru.
Solution: Promote hiking trails, highlight the unique moon-like landscape of jagged coral pinnacles, promote Japanese World War II relics as sites to visit, offer tourism packages which are a mix of visits to phosphate mines and World War II relics as well as fishing, diving and hiking activities.
Results: The number of tourists would increase by 14 percent per year.
Project 7: Not-So-Artificial Intelligence: How to Hack Your Memory (Real)
Problem statement: Developing memorization as a skill is essential to students and workers. However, strengthening the skill of memorization can be difficult, as everyone learns differently.
Goal statement: Use DMAIC to improve the efficiency of memorization by analyzing various memorization techniques. Efficiency was defined as the time it took for the task to be completed.
Solution: Team A was asked to memorize at will. Team B was asked to memorize based on three steps: 1) eliminate distracting environment, 2) identify and use individual’s learning-style preference (audio, visual, tactile) and 3) memorize words sequentially and in bite-size pieces rather than all at once.
Results: Team A improved only 11 percent, but Team B’s total time for memorization was reduced by 27 percent.

Project 8: Improve Efficiency of Making Cinnamon Rolls (Real)
Problem statement: It takes approximately three hours to make a batch of cinnamon rolls, and a lot of that time includes wait time.
Goal statement: Decrease the time it takes to make a batch of cinnamon rolls without significantly affecting the taste of the rolls.
Solution: Over half of the time spent making cinnamon rolls is spent waiting for the dough to rise or the actual time in the oven. To reduce this time, we need to find a new recipe without yeast, since that is the ingredient that makes bread rise and takes the majority of the time. An alternative recipe was developed.
Results: The time to make cinnamon rolls decreased from 185 minutes to 47 minutes, a 74 percent reduction in overall time. The taste did not appreciably change.
Why Should These Projects Matter to You?
These projects covered diverse subjects. Each group presented their project to a panel of judges, a crucial step in being certified as a White Belt. But there is no reason that these projects must stop at this level – they can be shared with businesses and individuals. The students hope these projects will serve as inspiration to solve problems of your own or to implement the experiments that these students used to solve the same or similar problems.
Click here to learn more about We Strive.
*Co-authored by students: Megha Marni, Sreya Chebrolu, Samantha Kamineni, Bhavika Lingutla, Chakri Vemulapalli, Hari Vemulapalli, Sriharsha Jaladhi, Aneesh Gottimukkala, Sumant Anantha and Sneha Nalluri.